気泡の長軸・短軸の算出
By K.Yoshimi
はじめに
CFDで気泡の挙動を解析した際に、気泡の長軸・短軸を求めたいことがあります。
しかし、気泡の形状は様々ですので、一般には長軸・短軸を定義するのが難しいかもしれません。
そこで、気泡を楕円体と仮定して、楕円体の長軸・短軸を求めるのも一案です。
楕円体の長軸・短軸の求めるアルゴリズム
CFDで計算した気泡の形状は、VOF法の界面形状として抽出したポリゴンデータとなるので、 気泡は、さまざまな位置に、さまざまな方向を向いた楕円状のポリゴンデータとなります。
それでは、このような楕円状のポリゴンデータの長軸・短軸を求めるにはどのような方法があるでしょうか?
分からないので、ChatGPTに質問してみた結果、以下の回答がありました。

モーメント法というのが面白そうなのでこれで実装してみましょう。
ParaViewによる楕円体の作成
例となる簡単な楕円体を作成するために、オープンソースのParaViewを使用します。
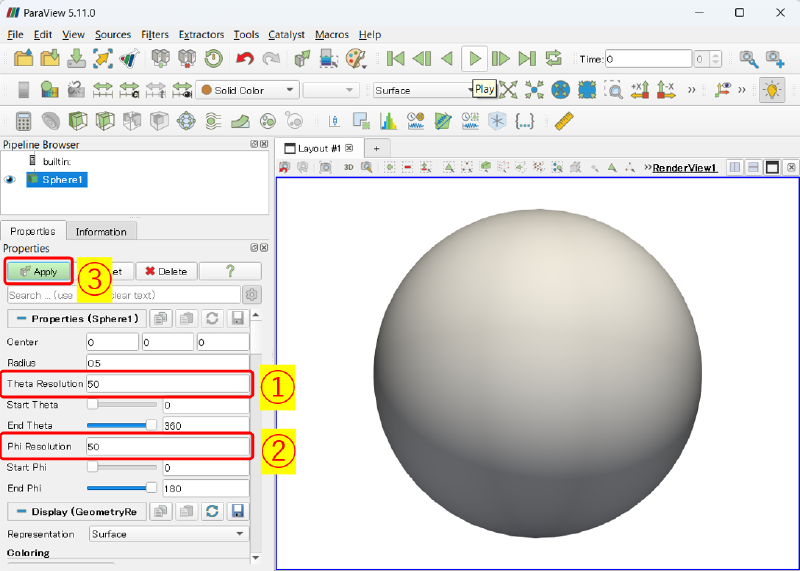
まず、楕円体を作成するために、球面を作成します。
Sources > Geometric Shapes > Sphere
で、Propertiesにおいて
- Theta Resolution : 50
- Phi Resoution : 50
として、Applyします。
次に、球面をTransoformフィルターで変形して、回転・平行移動します。
Filters > Alphabetical > Transform
で、Propertiesにおいて
- Translate : 10 10 10
- Rotate : 30 30 30
- Scale : 0.8 0.5 0.3
として、Applyします。
こうすると、x軸方向に0.8倍、y軸方向に0.5倍、z軸方向に0.3倍のスケーリングされ、 球面が楕円体になります。
それから、x軸周りに30度、y軸周りに30度、z軸周りに30度回転してから、x方向に10、y軸方向に、z軸方向に10平行移動しています。
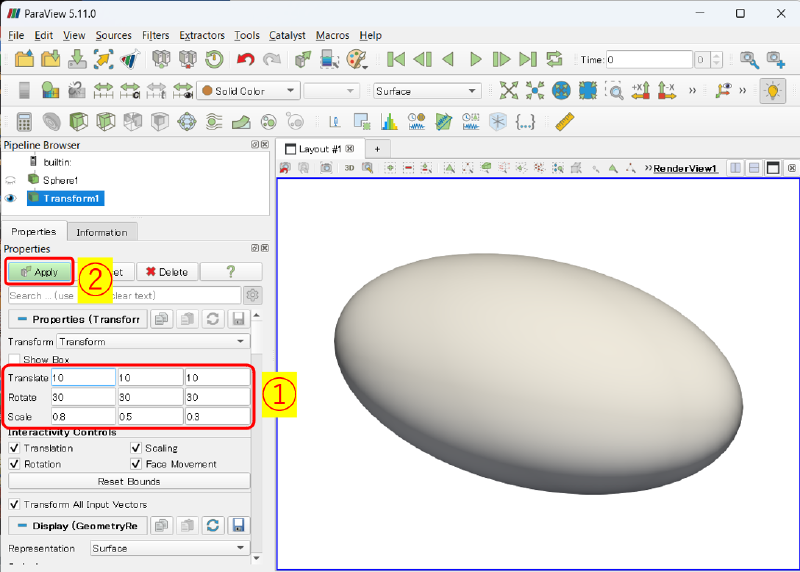
以上で、例となる楕円体が作成できました。
モーメント法による長軸・短軸の算出
モーメント法による長軸・短軸の算出も、簡単のためParaViewの、Programmable Filterで行ってみましょう。
Filters > Alphabetical > Programmable Filter
📌 Programmable Filterを使用すると、ParaView上でカスタマイズしたfilterをPythonで実装できます。
Programmable FilterのScriptに下記のような、 モーメント法で楕円体の長軸・短軸を算出するスクリプトを入力して、Applyします。
📌 モーメント法の実装方法はChatGPTに尋ねると教えてくれます。😄
import numpy as np
import vtk
def get_inertia_matrix(xyz):
# Moment of inertia tensor
x,y,z = xyz.T
Ixx = np.sum(y**2 + z**2)
Iyy = np.sum(x**2 + z**2)
Izz = np.sum(x**2 + y**2)
Ixy = -np.sum(x * y)
Iyz = -np.sum(y * z)
Ixz = -np.sum(x * z)
I = np.array([[Ixx,Ixy,Ixz], [Ixy,Iyy,Iyz], [Ixz,Iyz,Izz]])
return I
def get_axes(I):
# Calculate the eigenvectors.
eig = np.linalg.eig(I)
# Sort by order of increasing eigenvalues
eig_ids = np.argsort(eig[0])
eig_vals = eig[0][eig_ids]
eig_vecs = eig[1][eig_ids]
return eig_vals, eig_vecs
input0 = inputs[0]
pnts = input0.GetPoints()
length = input0.GetLength()
# Calculate the center of gravity point and then
# move the point cloud of the bubble to the origin.
com = np.mean(pnts, axis=0)
print(f'com {com}')
xyz = pnts - com
# Prepared to find the intersection of the bubble and the axis
obbtree = vtk.vtkOBBTree()
obbtree.SetDataSet(self.GetInput())
obbtree.BuildLocator()
# Assuming the bubble to be ellipsoid-like, obtain the major and minor axes.
I = get_inertia_matrix(xyz)
eig_vals, eig_vecs = get_axes(I)
print('eig_vecs:')
print(eig_vecs)
axes = vtk.vtkAppendPolyData()
axis_ids = []
for i in range(3):
# Determine the length of the axis by taking the
# intersection of the axial line and the bubble
pnt = eig_vecs[i] * length + com
intersects = vtk.vtkPoints()
obbtree.IntersectWithLine(com, pnt, intersects, None)
intersect = np.array(intersects.GetPoint(0))
r = np.linalg.norm(intersect-com)
print('r ', r)
# Create an axis
pnt1 = eig_vecs[i] * r
pnt2 = -1.0 * pnt1
line = vtk.vtkLineSource()
line.SetPoint1(pnt1+com)
line.SetPoint2(pnt2+com)
line.Update()
axis = line.GetOutput()
axes.AddInputData(axis)
axis_ids.append(i)
axes.Update()
output.DeepCopy(axes.GetOutput())
output.CellData.append(np.array(axis_ids), 'axis_id')
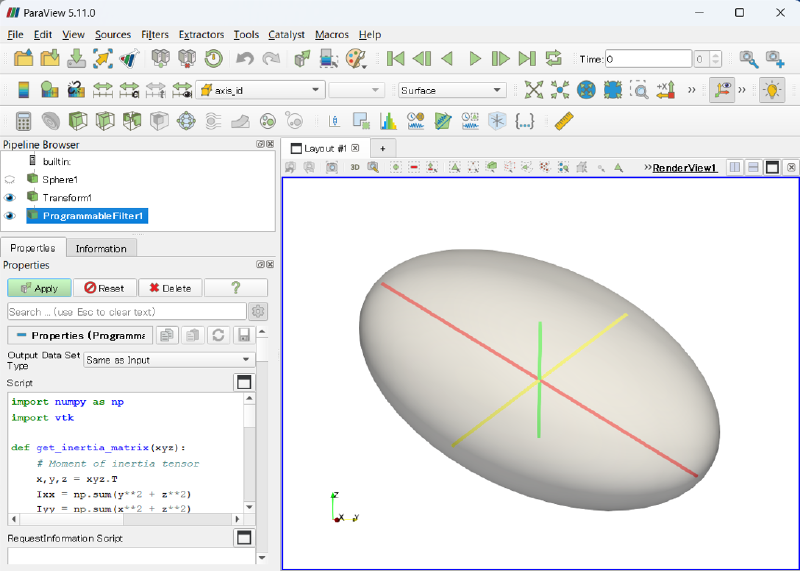
以上で、上手く長軸と短軸が算出できているようです。
おわりに
今回は、気泡形状を楕円体と見立てて長軸・短軸を算出しています。
実際の気泡形状に対しては、そんなに上手くいかないかもしれませんが、ぜひご参考にください。